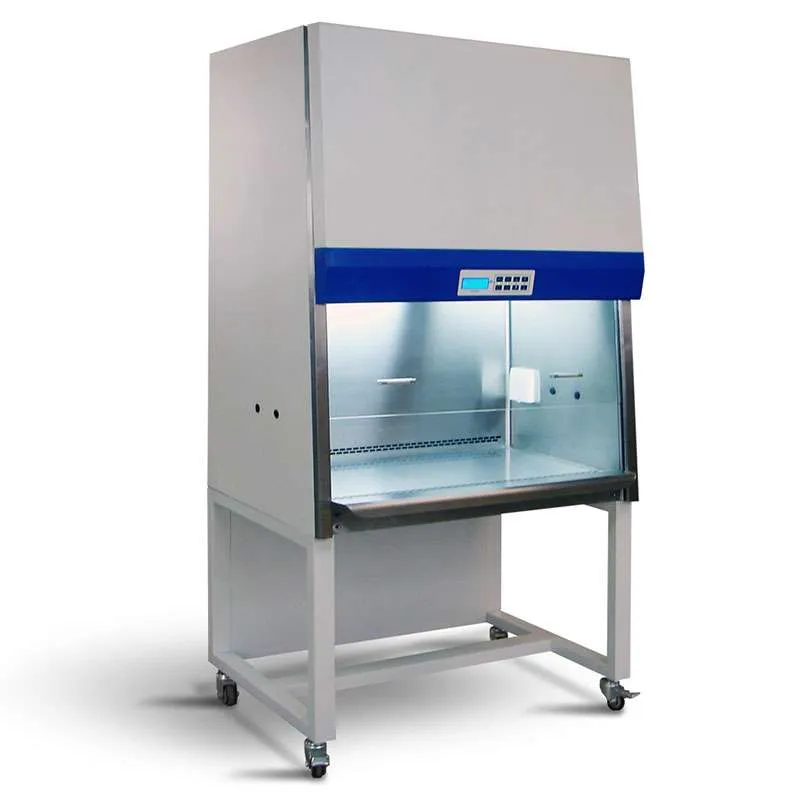

Biosafety Cabinet
Types of Biosafety Cabinet:
Class I- 100% Exhaust with Incineration.
Class II-A1- 100% Re-Circulation.
Class II-A2- 70% Re-Circulation & 30% Exhaust.
Class II-B1- 30% Re-Circulation & 70% Exhaust.
Class II-B2- 0% Re-Circulation & 100% Exhaust.
Class III- 100% Exhaust with Incineration & Glove Port.
Laminar Air Flow Cabinet: The working principle of the laminar flow hood after the air passes through the high-efficiency filter at a certain wind speed, a uniform flow layer is formed, so that the clean air flows in a vertical one-way, thus ensuring the high cleanliness required by the process in the working area.
Types of Laminar Air Flow Cabinet:
- Vertical Laminar Air Flow Cabinet.
- Horizontal Laminar Air Flow Cabinet.
Fume hood Cabinet: A fume hood is a ventilated, enclosed work space intended to capture, contain, and exhaust harmful or dangerous fumes, vapors, and particulate matter generated by procedures conducted within the fume hood.
Hot Air Oven: A hot air oven is a type of lab testing instrument that is used to heat up the products at a uniform temperature. A hot air oven is used to sterilize the product in a particular period of time under specific conditions like humidity, pressure, and other environmental factors.
Incubator: incubator, an insulated enclosure in which temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions can be regulated at levels optimal for growth, hatching, or reproduction. There are three principal kinds of incubators: poultry incubators, infant incubators, and bacteriological incubators. infant incubator.
BOD Incubator: A BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) incubator is a specialized laboratory equipment used in measuring the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms in water or wastewater samples. The BOD test is a widely used method to determine the level of water pollution and the effectiveness of treatment processes.
Autoclave: The autoclave works on the principle of moist heat sterilization where steam under pressure is used. to sterilize the material present inside the chamber. •The high pressure increases the boiling point of water and thus helps achieve a higher temperature. for sterilization.

Biosafety Cabinet
Types of Biosafety Cabinet:
Class I- 100% Exhaust with Incineration.
Class II-A1- 100% Re-Circulation.
Class II-A2- 70% Re-Circulation & 30% Exhaust.
Class II-B1- 30% Re-Circulation & 70% Exhaust.
Class II-B2- 0% Re-Circulation & 100% Exhaust.
Class III- 100% Exhaust with Incineration & Glove Port.
Laminar Air Flow Cabinet: The working principle of the laminar flow hood after the air passes through the high-efficiency filter at a certain wind speed, a uniform flow layer is formed, so that the clean air flows in a vertical one-way, thus ensuring the high cleanliness required by the process in the working area.
Types of Laminar Air Flow Cabinet:
- Vertical Laminar Air Flow Cabinet.
- Horizontal Laminar Air Flow Cabinet.
Fume hood Cabinet: A fume hood is a ventilated, enclosed work space intended to capture, contain, and exhaust harmful or dangerous fumes, vapors, and particulate matter generated by procedures conducted within the fume hood.
Hot Air Oven: A hot air oven is a type of lab testing instrument that is used to heat up the products at a uniform temperature. A hot air oven is used to sterilize the product in a particular period of time under specific conditions like humidity, pressure, and other environmental factors.
Incubator: incubator, an insulated enclosure in which temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions can be regulated at levels optimal for growth, hatching, or reproduction. There are three principal kinds of incubators: poultry incubators, infant incubators, and bacteriological incubators. infant incubator.
BOD Incubator: A BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) incubator is a specialized laboratory equipment used in measuring the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms in water or wastewater samples. The BOD test is a widely used method to determine the level of water pollution and the effectiveness of treatment processes.
Autoclave: The autoclave works on the principle of moist heat sterilization where steam under pressure is used. to sterilize the material present inside the chamber. •The high pressure increases the boiling point of water and thus helps achieve a higher temperature. for sterilization.
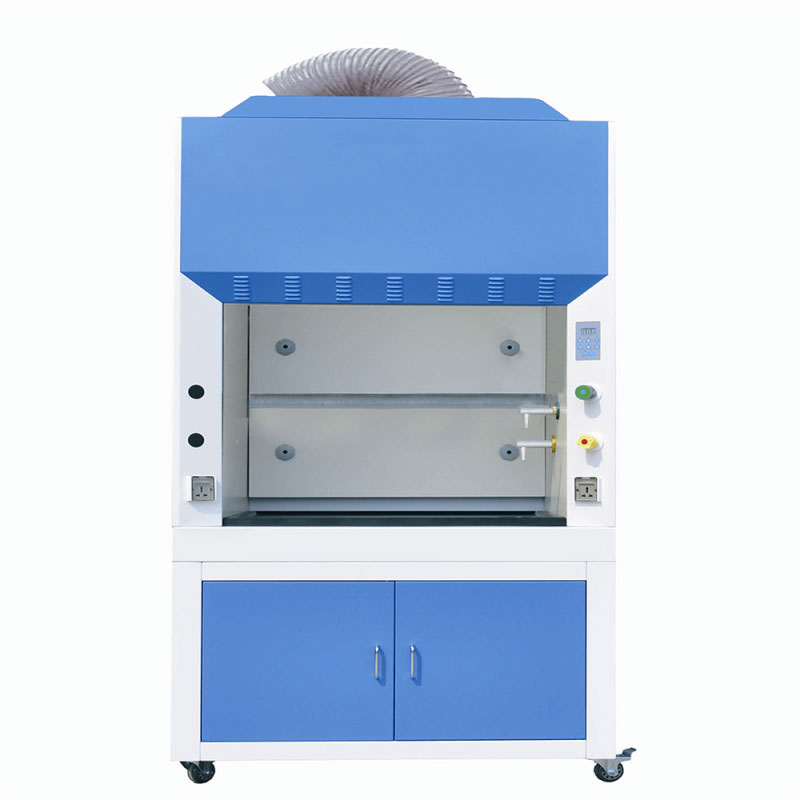
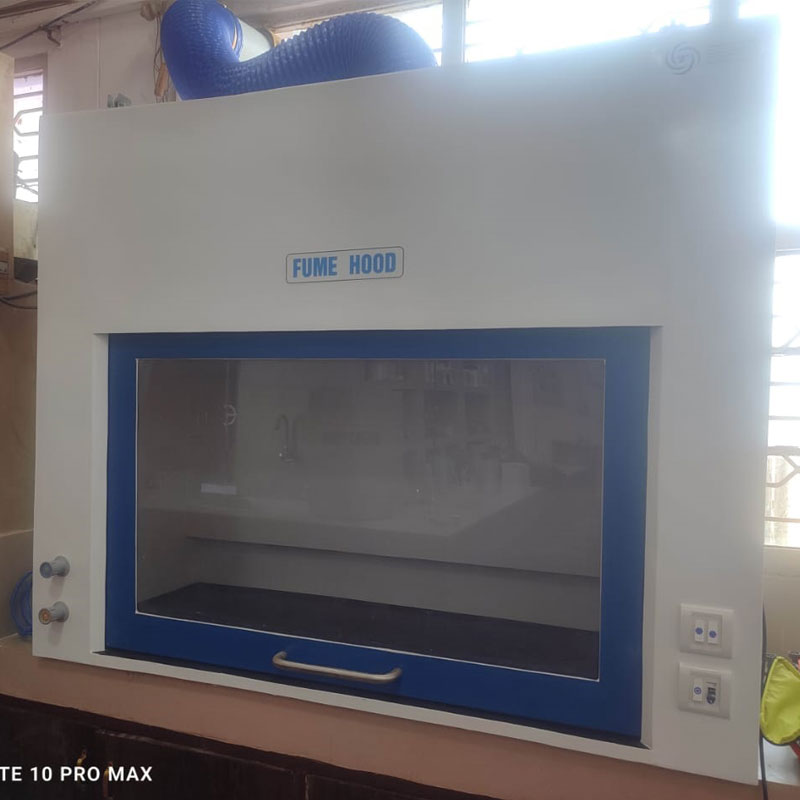


Fume Hood
Technomed Fume Exhaust Hood is constant supply air hood with auxiliary bye-pass provision. Three sides of the hood are permanently closed and the front side provided with sliding door with 4 mm polycarbonate sheet with suitable frame. Technomed fume hoods are provided with a specially designed under-bench storage shelf, which acts as a support-stand for the hood as well as provides a large space for keeping reagent bottles, small instruments etc. Each under-bench module is provided with top drawer and a horizontal partition and lockable doors.These modules are fabricated by using galvanized iron sheet and finished poly-urethane paint over three coating of surface primer.
Inside the working chamber, there will be a sturdy baffle provided at about 300mm above the work-table to uniformly direct the fumes / odor / smoke directly in to the hood’s exhaust system. Suction will be done at three different levels suitable for mild to heavy fumes.
Technomed fume chamber will be provided with a powerful centrifugal blower, mounted on top of the Hood,suitably designed to create necessary suction pressure so as to force the fumes from the hood to exhaust out in to the atmosphere through the duct. The blower and casing will be made of mild steel with polyurethane paint coated /FRP finish.
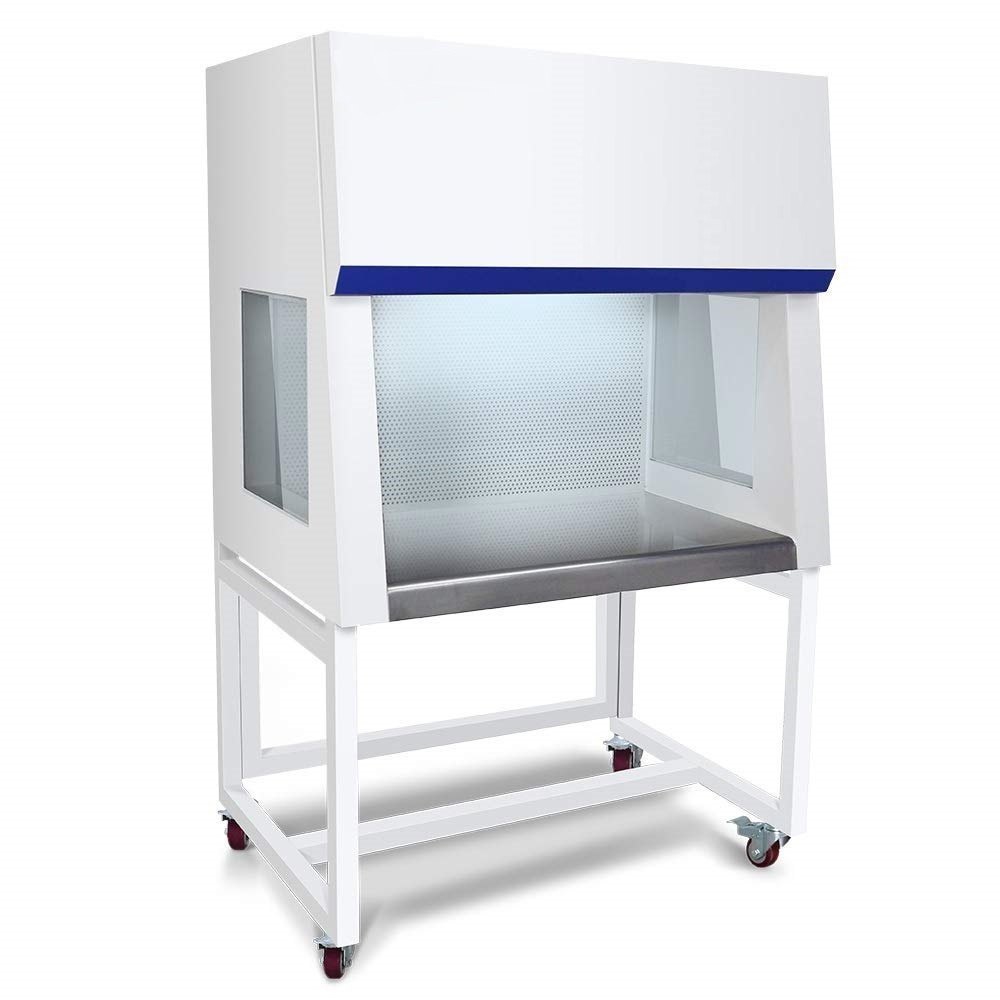

Horizontal Laminar Air Flow
Vertical Laminar Airflow system allows operation in sterile and particle free conditions because the continuous flushing of the working area by a unidirectional and Vertical and ultra filtered airflow, it assures a full product protection.
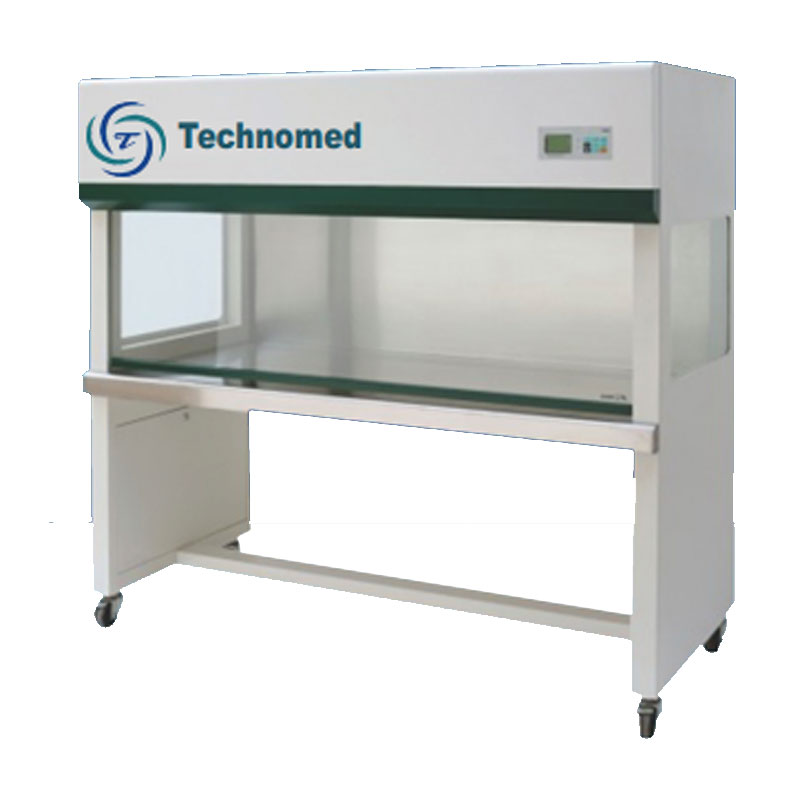

Vertical Laminar Air Flow
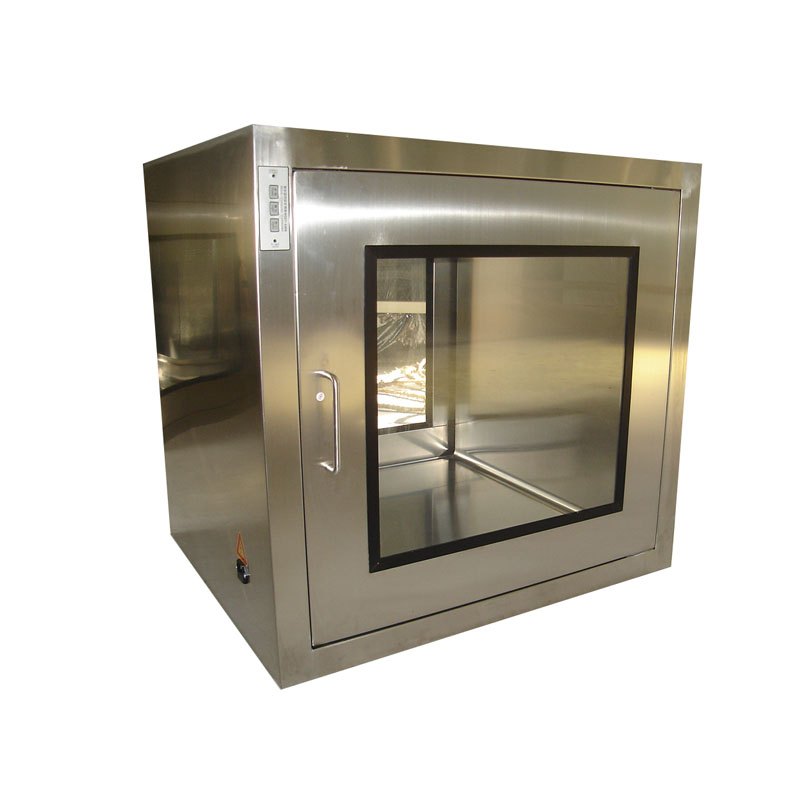

Static Pass Box
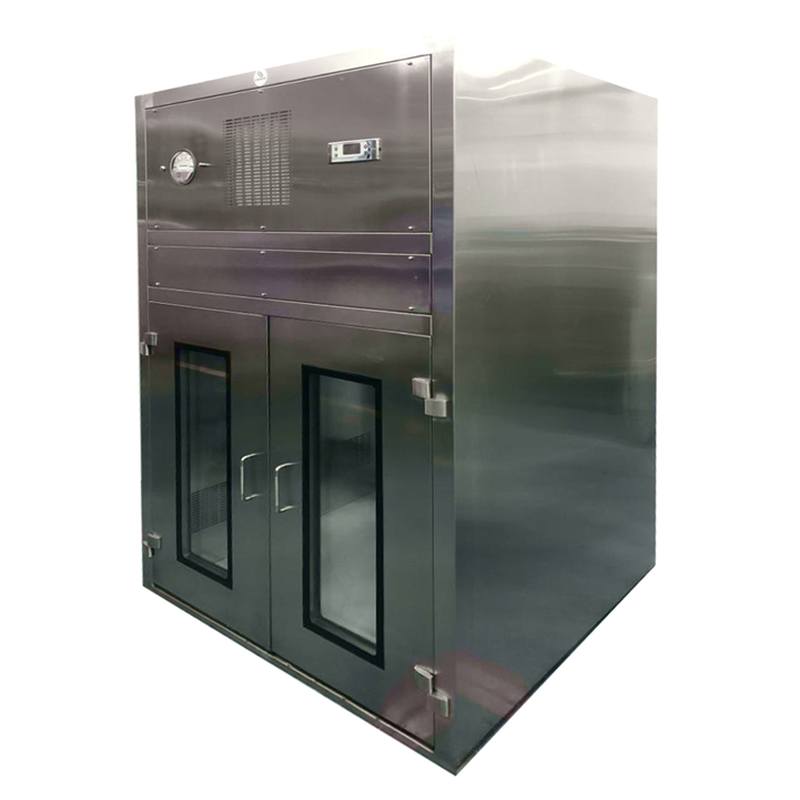

Dynamic Pass Box
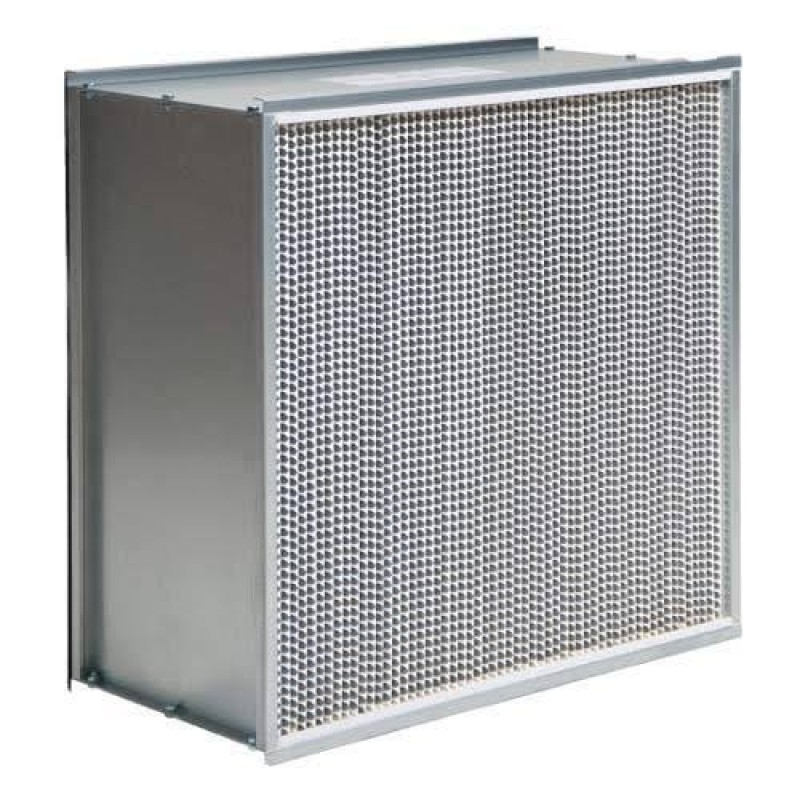

Hepa Filter
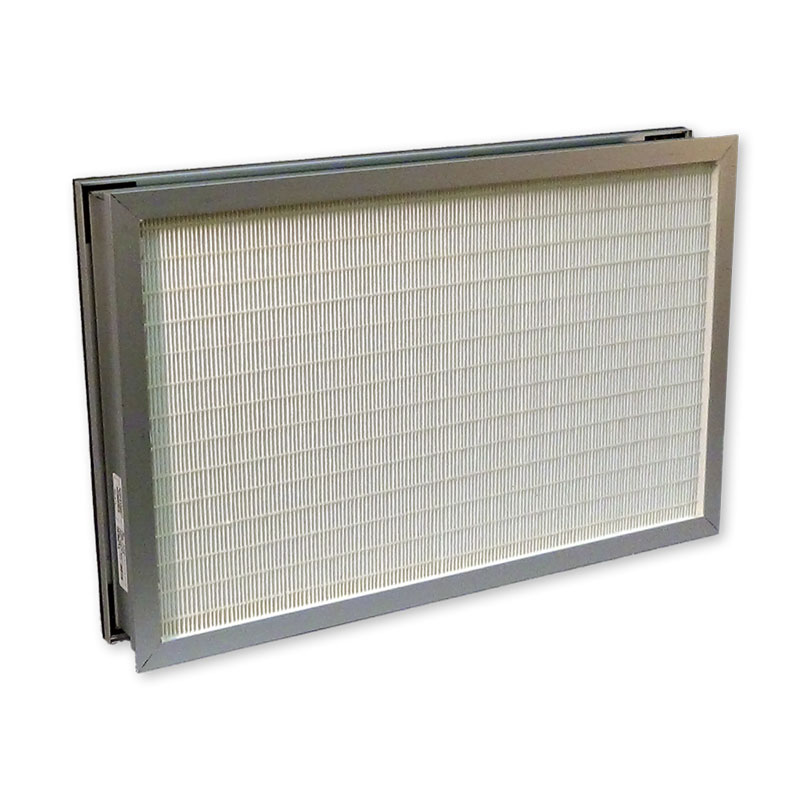

Pre Filter
Pre-filters are often overlooked but play a crucial role in air filtration as the first defense against indoor pollutants. Some pre-filters offer more benefits than expected: they can deodorize the air, capture larger airborne particles, and help prolong the life of your HEPA filter.
Air purifiers equipped with pre-filters allow you to better control the air quality for your loved ones and guests. For example, Honeywell activated carbon pre-filters can help remove gases and common household odors, such as those from cooking or pets. Combining an air purifier with both HEPA filtration and pre-filtering provides a powerful solution for cleaner air.
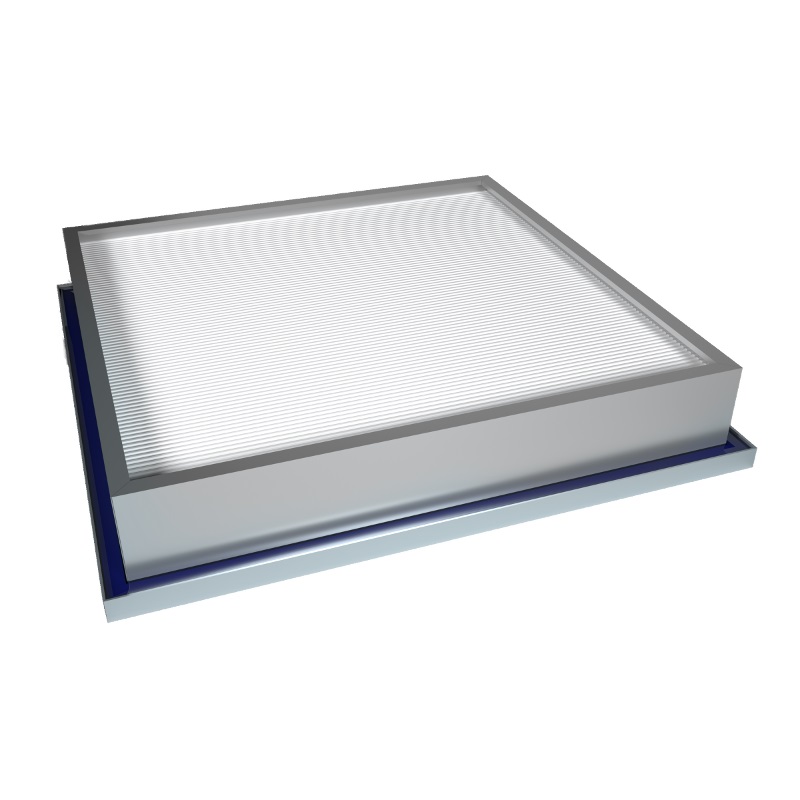
Ultra Filter
The Ultra Filter utilizes an advanced process called Ultrafiltration, employing membrane filtration technology and hydrostatic pressure. It is designed to retain high molecular weight substances and is available in both spiral-wound and tubular configurations. This specialized filter is suitable for various process applications, particularly for removing particulates and macromolecules.
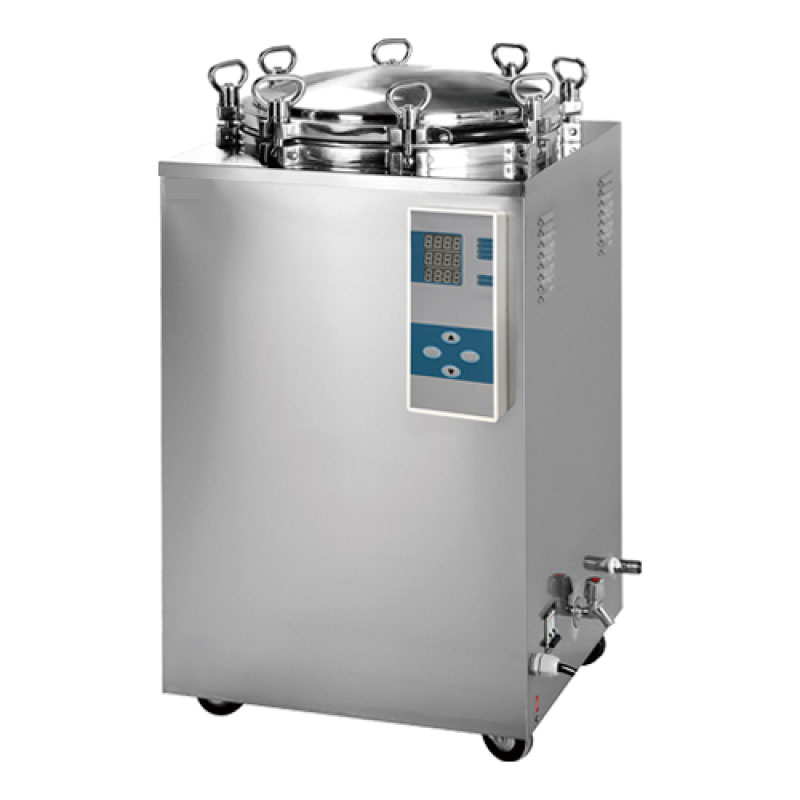

Autoclave
Autoclaves, commonly referred to as steam sterilizers, are machines primarily used in healthcare and industrial settings. They operate by using steam under pressure to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on items placed within a pressure vessel. These items are heated to a specific sterilization temperature for a set duration. The steam's moisture effectively transfers heat to the items, breaking down the protein structure of bacteria and spores.
In healthcare, "autoclave" is the term often used to describe a Steam Sterilizer. According to ANSI/AAMI4, which provides standards and guidelines for medical device processing, autoclaves in healthcare are specifically termed Steam Sterilizers.
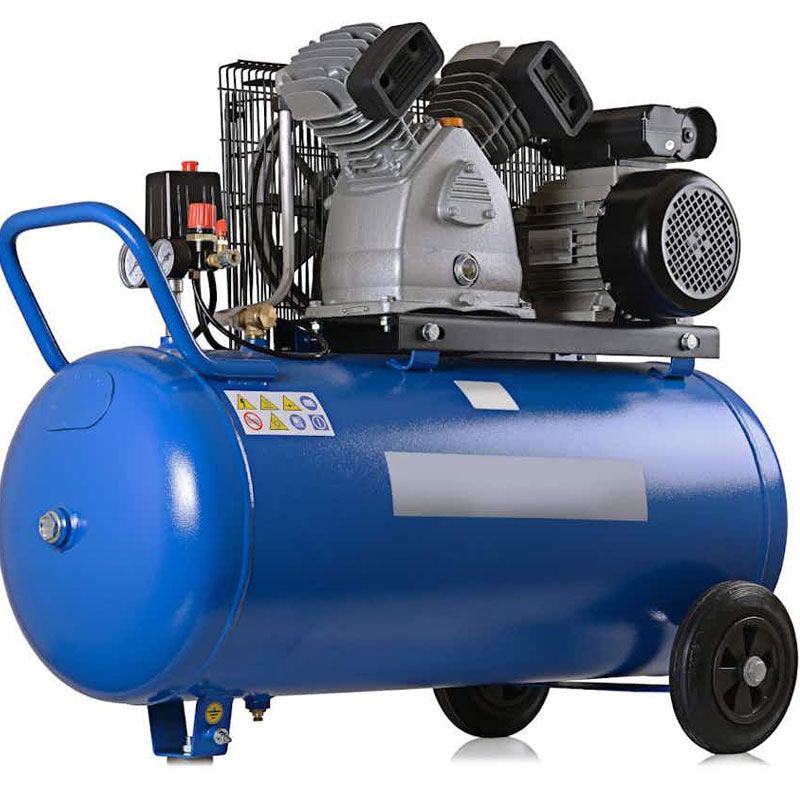

Compressor
A compressor is a device that increases gas pressure by mechanically reducing its volume. While air is the most commonly compressed gas, other important gases like natural gas, oxygen, and nitrogen are also compressed. Compressors generally fall into three categories: positive displacement, centrifugal, and axial. Positive displacement compressors, often of the reciprocating piston type, work by drawing in gas during the piston's suction stroke, compressing it by reducing its volume as the piston moves in the opposite direction, and then discharging it when the gas pressure surpasses the outlet valve pressure. Reciprocating compressors are particularly useful for delivering small quantities of gas at relatively high pressures.
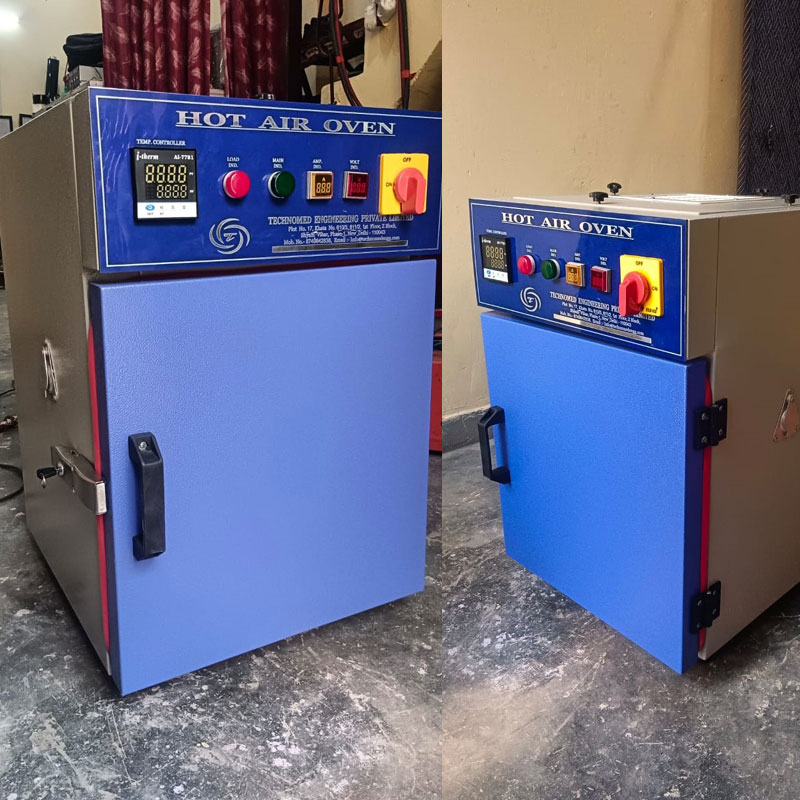

Hot air oven
A hot air oven is a laboratory instrument used for various applications across multiple industries. This device, powered by advanced technology, is primarily used to sterilize products using dry heat. Its triple-walled construction allows it to operate quietly and efficiently.
Dry heat is ideal for sterilizing metal instruments that may rust or dull in the presence of water vapor. A thermostat controls the temperature within the inner chamber for the necessary duration, while air circulating fans ensure even heat distribution.
Hot air ovens are becoming increasingly popular because they do not require water or pressure to build up inside the oven, making them especially useful for sterilization in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and hospital industries.
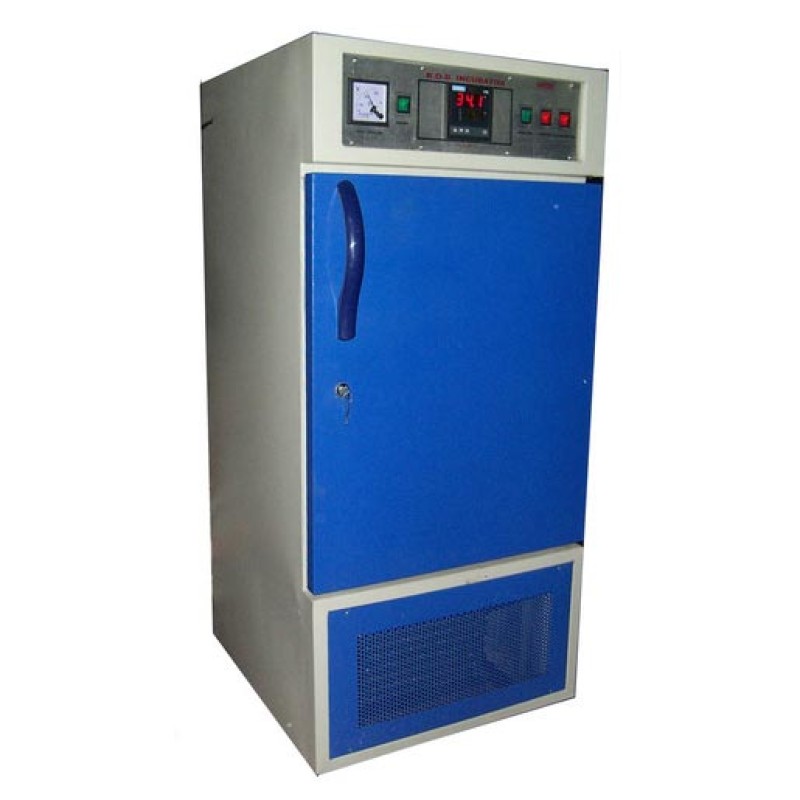

BOD incubator
BOD incubators are widely used across various industries to create a controlled environment with a temperature of 20°C. These incubators are essential for testing products at specific temperatures to measure biochemical oxygen demand. They are also used for germination studies, bacterial culturing, and research on insects and microorganisms. To ensure optimal performance over time, it is crucial to maintain the incubator properly. Manufacturers of BOD incubators use high-quality materials to ensure durability.
It is advisable to disconnect the power supply when the incubator will not be in use for extended periods. Regular servicing is essential to maintain optimal functioning and prevent machine downtime. Always read the instruction manual and catalog carefully before use, and avoid exceeding the recommended usage cycle, as overuse can shorten the machine's lifespan.
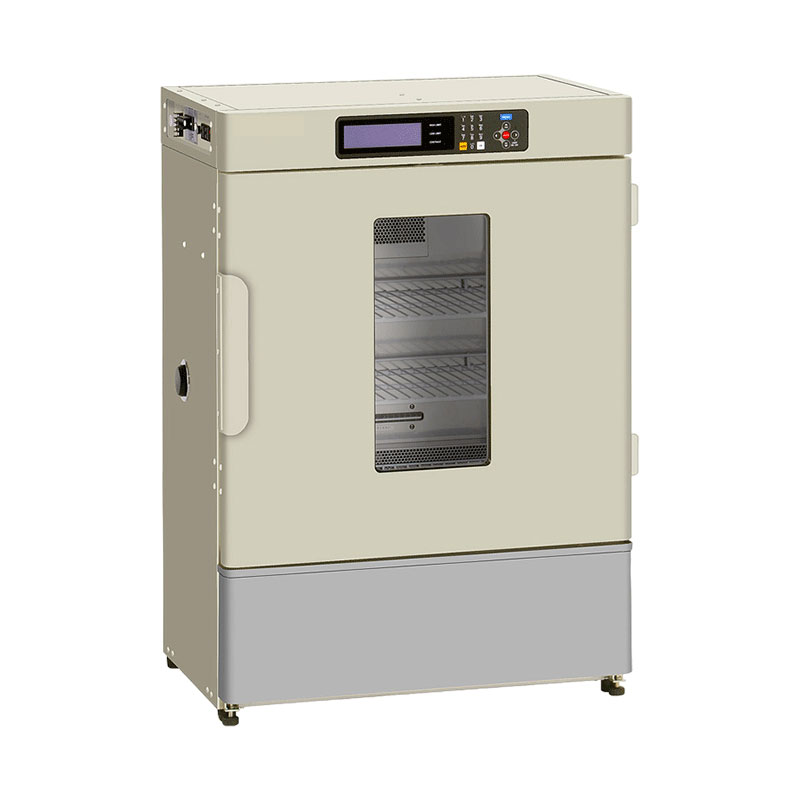

Incubator
A BINDER incubator is an ideal choice for reliable incubation processes. Whether equipped with natural or forced convection, these incubators are designed to meet the growth and incubation needs of microbiological cultures. They ensure consistent, reproducible results for every routine laboratory test, even with high batch volumes and extended operation.
Featuring advanced APT.line™ technology, this new generation of incubators offers exceptional efficiency and precise temperature control, making them highly appealing for laboratory use.
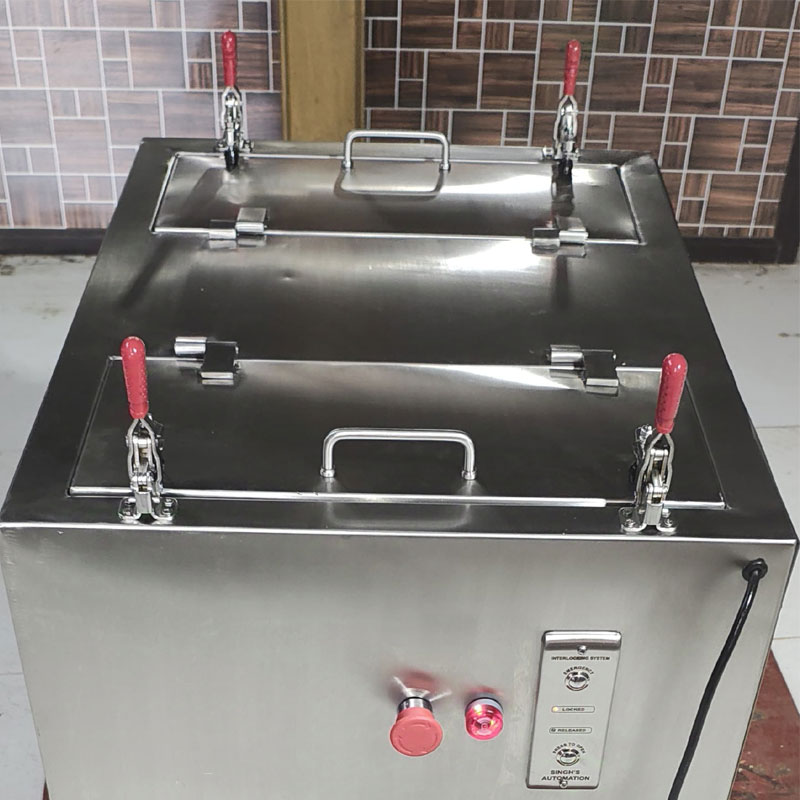

Dunk Tank
Dunk tanks can incorporate various scientific principles and specialized equipment depending on their complexity and use. While the traditional dunk tank is a simple mechanical setup, here’s an overview of scientific types of equipment and features that might be used in advanced or unique dunk tanks:
Applications in Scientific Studies
Biomechanics: Studying throwing techniques and force dynamics.Hydrodynamics: Analyzing splash patterns or water displacement.Physics Education: Demonstrating principles like gravity, momentum, and mechanical advantage.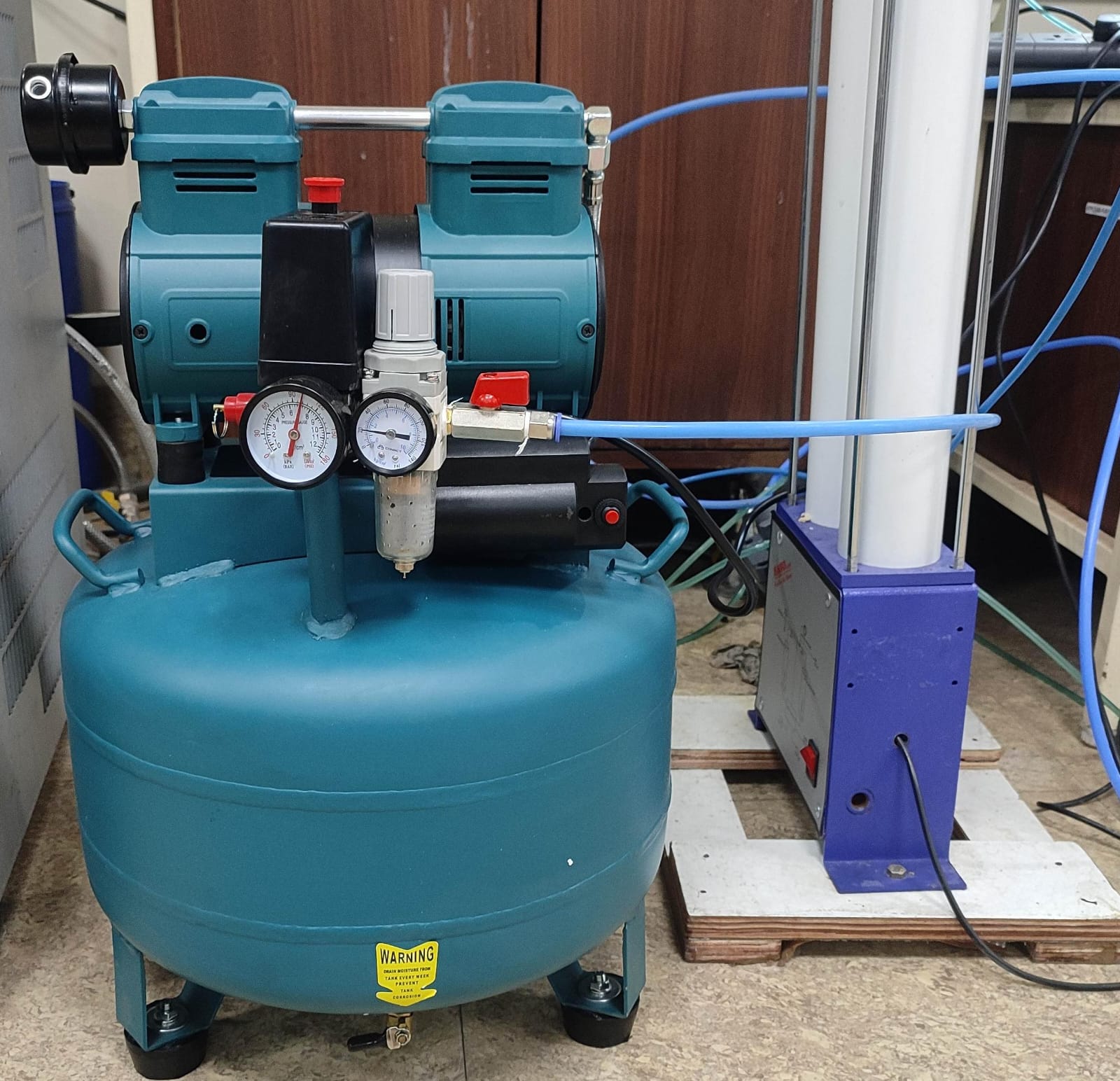
Oil Free Compressors
An oil-free air compressor is a type of compressor that does not use oil for lubrication during its operation. This makes them ideal for applications where air quality is critical.
Advantages of oil-free compressors:
Pure air output: No risk of oil contamination in the compressed air.
Reduced maintenance: Fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes.
Environmental friendliness: No oil disposal issues.
Improved energy efficiency: Some oil-free compressors are more energy-efficient than oil-lubricated models
